Introduction
For this post, you will explore the process of development for the game of pong. one of the four major features of our project: TripleAJ Arcade
Additionally this post will explore and try to fulfill as many CPT requirements issued by CollegeBoard.
This post will also explore the other features we worked on outside of our games as well.

Video
CPT Submission - 3A
3.a.i
My program presents an an interactive arcade game called, “Pong” to serve as entertainment for the user.
3.a.ii
The user must first pay 10 AJ Tokens (our arcade currency system) in order to play Pong, this will be at the start screen that we decided.
The program allows a user to play ping pong against an AI, there are two paddles constantly hitting a ball to one another. Whoever scores 7 first, wins!
If the user loses, he/she/they have lost 10 tokens from their total balance. If the user wins, they win 15 tokens for beating the AI, the 15 tokens will be added to their balance along with the 10 tokens reimbursed when the user paid to play at the start. This will be seen at the end screen, the user will also have an option to play the game again in efforts to win their tokens back or to simply have fun.
3.a.iii
The controls for my game is simply the mouse moving up and down. We believe controlling the mouse is the easiest way to play the game rather than constantly clicking, “W/A/S/D”.
The input for our login system (we discuss this later) is your UID, password, and username.
CPT Submission - 3B
3.b.i - Token System Code For Pong
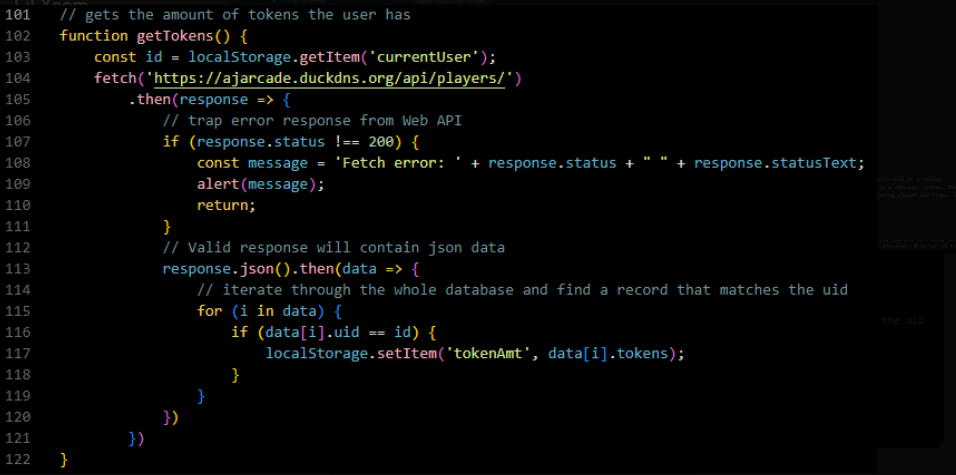
3.b.ii - Removing Tokens
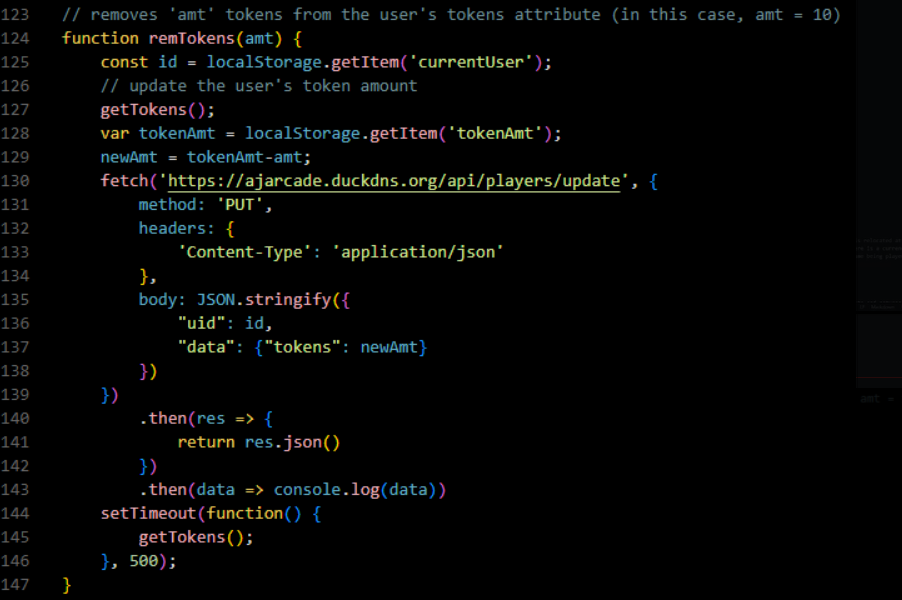
3.b.iii
The variable representing local storage is “tokenAmt”. For the first block, tokenAmt is in 117 and tokenAmt for localstorage in the second blog is found in line 128.
3.b.iv
The information that is saved in the local storage as tokenAmt is crucial for the program to function properly. It indicates the total number of tokens that the user possesses, which is required for carrying out mathematical operations to update the token balance after the user has played the game and earned more tokens based on their performance. Therefore, this data plays a key role in the proper functioning of the program.
3.b.v
The current use of local storage in the program is a reliable and efficient method for storing and updating the user’s token balance. This approach allows for easy retrieval and modification of data, making it a simple and effective way to manage the user’s token balance. However, an alternative approach could involve fetching the user’s token balance every time the game requires an update. This alternative approach would not be as efficient, as it would require more computing power and would be less convenient to update. Therefore, local storage is the preferred option, as it offers a more streamlined and efficient solution to managing the user’s token balance.
CPT Submission - 3C
3.c.i
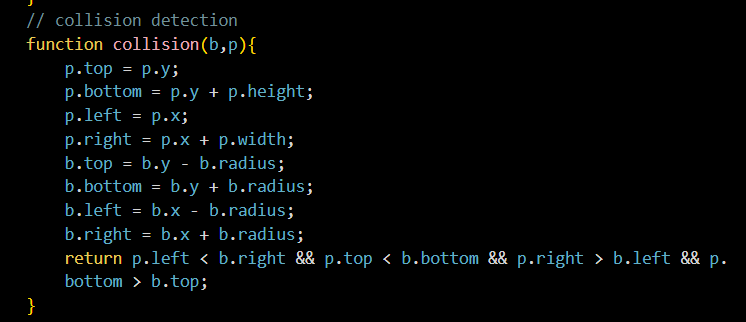
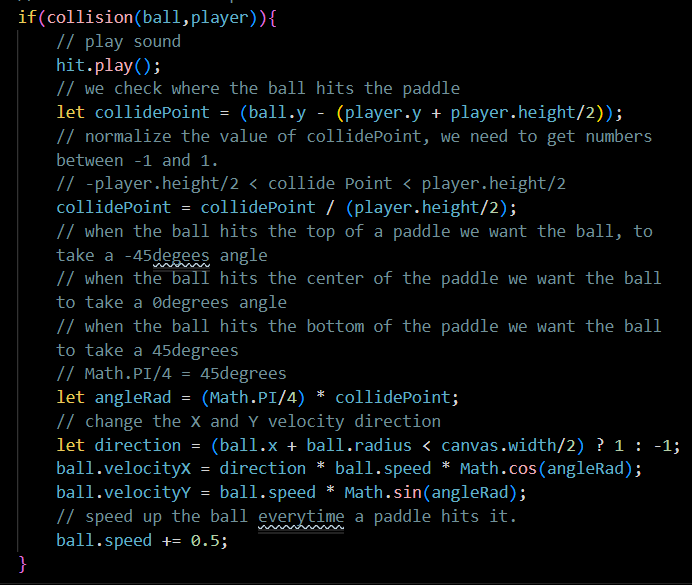
3.c.ii
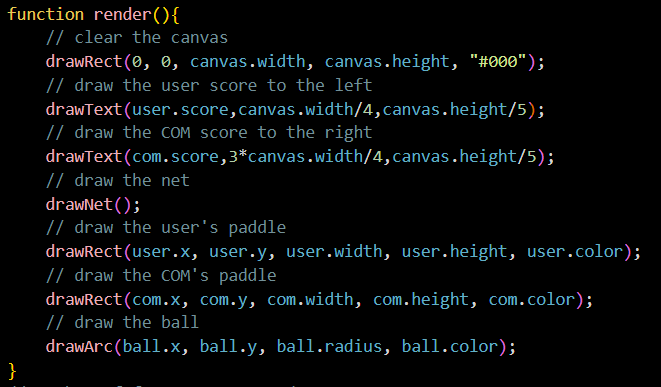
3.c.iii
The first code block demonstrates a function called “collision” that accepts two parameters “b” and “p”. The function is used to detect a collision between a ball and a paddle in the game of Pong.
To achieve this, the function determines the top, bottom, left, and right positions of both the ball and the paddle and checks for overlapping positions between them. The function returns a Boolean value indicating whether a collision has occurred or not, based on the four boundaries of the ball and paddle.
This function plays a crucial role in the Pong game mechanics as it enables the game to detect and respond to collisions between the ball and paddle objects. The use of this function is an example of procedural abstraction, as it abstracts away the details of the collision detection process, allowing the programmer to focus on other aspects of the game development.
The second code block checks for collisions between the ball and the player paddle in the game of Pong, using a “collision” function. If a collision is detected, the code plays a sound effect, calculates the point of collision, and uses it to determine the angle of reflection for the ball using different functions. It then determines the direction of the ball based on which half of the paddle it collided with, updates the velocity of the ball with the new angle and direction, and increases its speed to simulate acceleration.
3.c.iv - Selection, Iteration, Sequencing
This code has sequencing because it executes a series of steps in a particular order to render the game of Pong on the canvas. First, it clears the canvas using the “drawRect” function with a black color. Then, it draws the user’s score on the left side of the canvas and the computer opponent’s score on the right side of the canvas using the “drawText” function.
After that, it draws the net using the “drawNet” function, which can be seen as a dotted line that is constantly looping and resetting after every score, this is shown as iteration.
Next, it draws the user’s paddle and the computer opponent’s paddle using the “drawRect” function with their respective properties. Finally, it draws the ball using the “drawArc” function with its position and radius. Through what I explained just now, there is selection in the function render() code block as it uses conditional statements to decide which direction the ball will move and whether the player or the computer has scored.
CPT Submission - 3D
3.d.i - Calls for CRUD
Create: When a new user registers on your website, a POST call is made to the backend to create a new user account. The user provides their email address and a password, which are stored in the backend database. The server then generates a unique user ID and returns it to the client as a response.
Read: When a user logs in to your website, a GET call is made to the backend to retrieve their account information. The server checks the user’s email and password against the database, and if the credentials are valid, the server returns the user’s account information (including their current token balance) to the client.
Update: When a user updates their password, a PUT call is made to the backend to update the user’s account information in the database. The user provides their old password and a new password, and the server checks that the old password is valid before updating the user’s account information with the new password.
Delete: If a user chooses to delete their account, a DELETE call is made to the backend to delete the user’s account information from the database. The server checks the user’s email and password against the database to verify their identity before deleting their account information.
3.d.ii - Calls for Conditions
-
First call test the conditions and has idiot proofing for sign up, checks everything and then also verifies if the user has enough tokens to play pong.
-
Second call for conditions is to verify that the backend has received an update in token balance, and that update will be sent to the frontend, to our leaderboard.
3.d.iii - Results of Calls
-
First call results - Allows uers to create account, play games, view leaderboard, earn tokens, etc.
-
Second call resultS: Allows website to be updates through JS fetch and allows for all users to see the website constantly updating and functioning.