- wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidenhuynh/CS_Swag/master/_notebooks/2022-11-30-randomvalues.ipynb
- Libraries
- Homework (part 1)
- Homework (part 3)
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidenhuynh/CS_Swag/master/_notebooks/2022-11-30-randomvalues.ipynb
Libraries
- A library is a collection of precompiled codes that can be used later on in a program for some specific well-defined operations.
- These precompiled codes can be referred to as modules. Each module contains bundles of code that can be used repeatedly in different programs.
- A library may also contain documentation, configuration data, message templates, classes, and values, etc.
Why are libraries important?
- Using Libraries makes Python Programming simpler and convenient for the programmer.
- One example would be through looping and iteration, as we don’t need to write the same code again and again for different programs.
- Python libraries play a very vital role in fields of Machine Learning, Data Science, Data Visualization, etc.
A few libraries that simplify coding processes:
- Pillow allows you to work with images.
- Tensor Flow helps with data automation and monitors performance.
- Matplotlib allows you to make 2D graphs and plots.
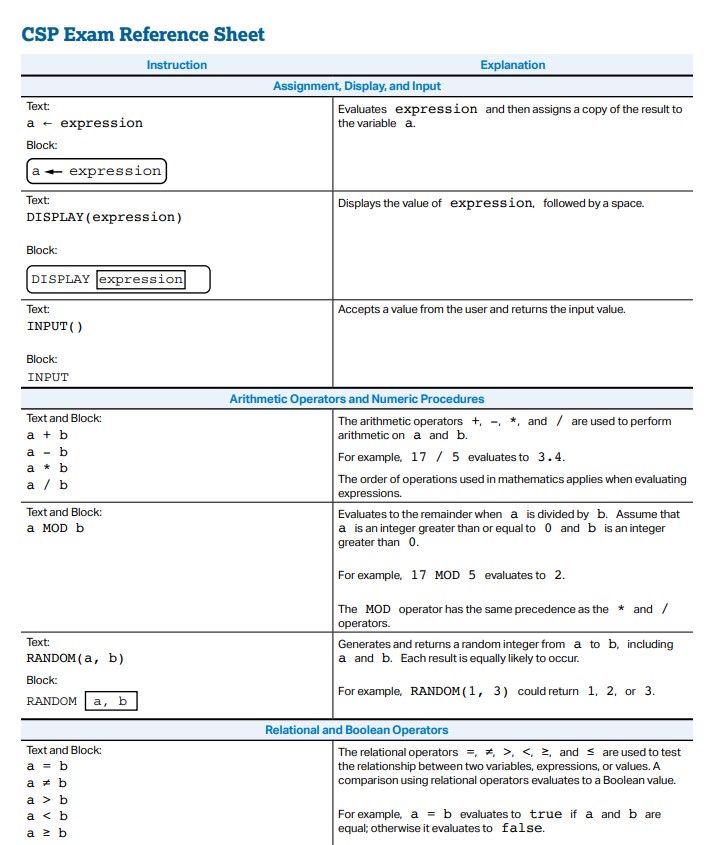
The AP Exam Refrence Sheet itself is a library!
Hacks:
Research two other Python Libraries NOT DISCUSSED DURING LESSON and make a markdown post, explaining their function and how it helps programmers code.
API’s
- An Application Program Interface, or API, contains specific direction for how the procedures in a library behave and can be used.
- An API acts as a gateway for the imported procedures from a library to interact with the rest of your code.
Activity: Walkthrough with NumPy
Install NumPy on VSCode: Open New Terminal In VSCode: pip3 install --upgrade pip pip install numpy
REMEMBER: When running library code cells use Python Interpreter Conda (Version 3.9.12)
Example of using NumPy for arrays:
import numpy as np
new_matrix = np.array([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],[7, 8, 9]])
print (new_matrix)
import numpy as np
# defining polynomial function
var = np.poly1d([2, 1])
print("Polynomial function, f(x):", var)
# calculating the derivative
derivative = var.deriv()
print("Derivative, f(x)'=", derivative)
# calculates the derivative of after
# given value of x
print("When x=5 f(x)'=", derivative(5))
Random Values
- Random number generation (RNG) produces a random number (crazy right?)
- This means that a procedure with RNG can return different values even if the parameters (inputs) do not change
- CollegeBoard uses
RANDOM(A, B), to return an integer between integersAandB.- RANDOM(1, 10) can output 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, or 10
- In Python, this would be
random.randint(A, B), after importing Python's "random" library (import random) - JavaScript's works a little differently, with
Math.random()returning a value between 0 and 1.- To match Python and CollegeBoard, you could make a procedure like this
CollegeBoard Example: What is the possible range of values for answ3

import random # Fill in the blank
def Dice(n):
sum = 0
while n != 0:
sum = sum + random.randint(1, 6)
n = n - 1
return sum
Dice(5) # Will output a range of 5 to 30
Homework
-
Write a procedure that generates n random numbers, then sorts those numbers into lists of even and odd numbers (JS or Python, Python will be easier).
-
Using NumPy and only coding in python cell, find the answer to the following questions: a. What is the derivative of 2x^5 - 6x^2 + 24x? b. What is the derivative of (13x^4 + 4x^2) / 2 when x = 9?
-
Suppose you have a group of 10 dogs and 10 cats, and you want to create a random order for them. Show how random number generation could be used to create this random order.
import random
def sort_random_numbers(n: int) -> tuple:
# Generate n random numbers
numbers = [random.randint(0, 100) for _ in range(n)]
# Sort numbers into even and odd lists
even_numbers = [x for x in numbers if x % 2 == 0]
odd_numbers = [x for x in numbers if x % 2 == 1]
return (even_numbers, odd_numbers)
even_numbers, odd_numbers = sort_random_numbers(10)
print(even_numbers) # [2, 8, 12, 28, 60, 82] (example)
print(odd_numbers) # [1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13] (example)
import numpy as np
#LMAOOO i just used coefficient, this work tho fr
p = np.poly1d([2, 0, -6, 24, 0])
derivative = p.deriv()
# Printing the final derivative boys
print(derivative)
import numpy as np
def calculate_derivative(x: float):
poly = np.array([13, 0, 4, 0, 0])
derivative = np.polyder(poly)
result = np.polyval(derivative, 9)
return result
print(calculate_derivative(9))
import random
dogs = ['Blue 1', 'Blue 1', 'Blue 3', 'Blue 4', 'Blue 5', 'Blue 6', 'Blue 7', 'Blue 8', 'Blue 9', 'Blue 10']
cats = ['Red 1', 'Red 2', 'Red 3', 'Red 4', 'Red 5', 'Red 6', 'Red 7', 'Red 8', 'Red 9', 'Red 10']
colors = []
for blue in dogs:
colors.append((blue, random.randint(1, 20)))
for red in cats:
colors.append((red, random.randint(1, 20)))
colors.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
for color in colors:
print(color[0])